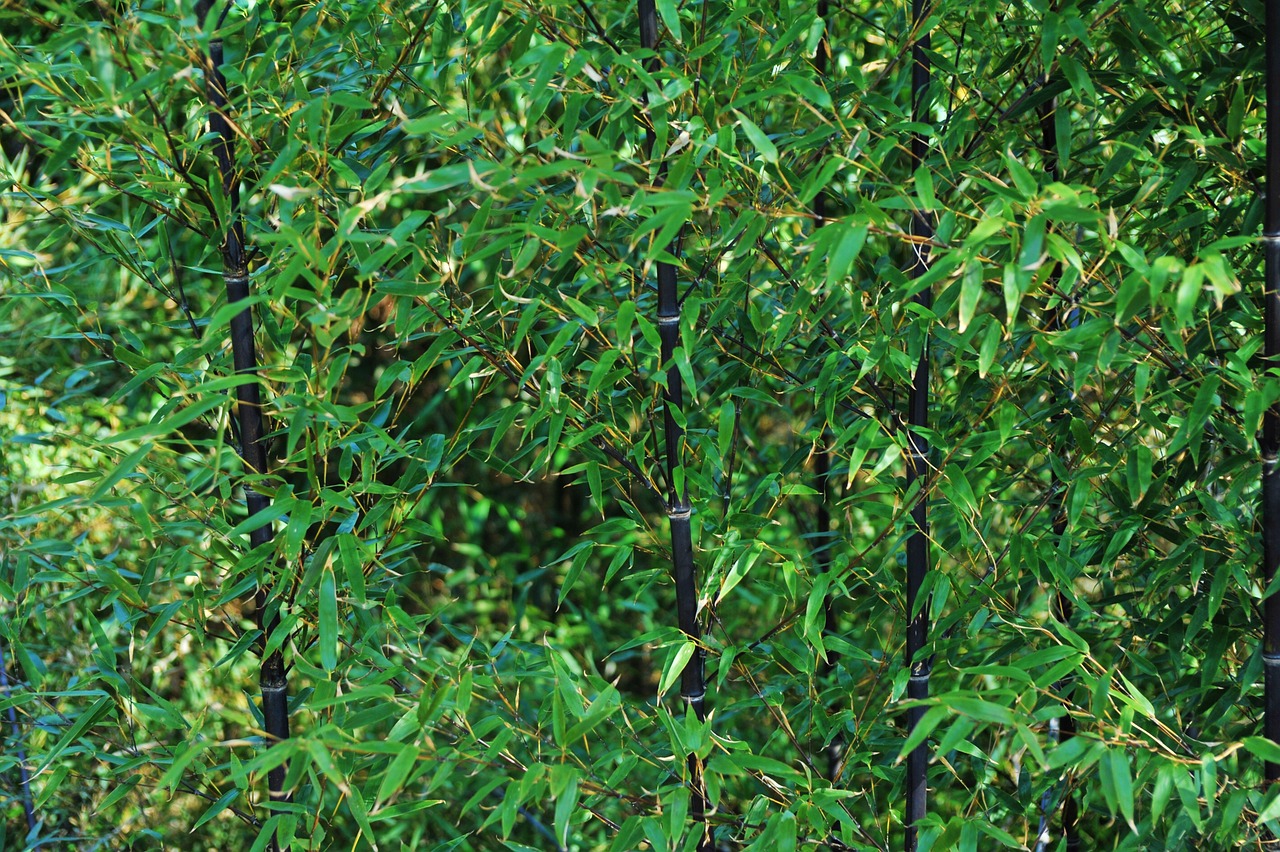
How to Plant Bamboo
Bamboo, with its elegant stature and versatile applications, has captured the imagination of gardeners worldwide. Whether you’re drawn to its rapid growth, its role as a privacy hedge, or its aesthetic appeal in landscaping, understanding how to cultivate bamboo successfully is crucial. This guide delves into the nuances of bamboo types, planting techniques, and maintenance strategies to help you harness the full potential of this remarkable plant.
Bamboo Types:
Bamboo species fall into two main categories, each with unique growth habits and care requirements:
- Monopodial (Runner) Bamboo: Known for its vigorous spreading habit, runner bamboo is ideal for creating dense hedges or ground covers. However, its invasive nature requires careful management.
- Sympodial (Clumping) Bamboo: Clumping bamboo grows in tight clusters, making it easier to contain and ideal for container gardening or as a non-invasive garden plant.
Choosing the Right Bamboo:
- For hedgerows, runner bamboo is your best bet, while clumping bamboo suits container gardening due to its manageable growth pattern.
- Consider the mature size of the bamboo variety you select, as some can reach up to 20 feet tall. Research the specific characteristics of your chosen species to ensure it aligns with your gardening goals.
Basic Pointers on How to Plant Bamboo:
- Preparing the Soil: Start by clearing the site of weeds and incorporating rich, loose soil. Bamboo thrives in well-draining conditions without the need for heavy fertilization, which can harm the plants.
- Planting and Watering: Plant rhizomes a few inches deep or set container plants level with their previous soil line, typically around 3 inches deep. Maintain moist soil conditions without overwatering. Bamboo leaves curling is a sign of dehydration.
- Sun Exposure and Fertilization: Bamboo prefers sunlight but can tolerate partial shade, offering flexibility in location choice. Use a general-purpose fertilizer monthly during the growing season for optimal health.
- Managing Growth: For runner bamboo, consider planting near water features or using sidewalks as natural barriers to control spread. A deep edging of about 30 inches can further prevent unwanted expansion.
Tips and Warnings:
- Pest and Disease Management: Stay vigilant for signs of pests or diseases. Utilize recommended insecticides and fungicides from trusted sources to protect your bamboo without harming it.
- Moisture is Key: Bamboo rhizomes require consistently moist soil for survival and growth. Initial growth may be slow, but with proper care, bamboo will flourish, showing rapid growth in subsequent years.
- Growth Control: Limit watering and fertilization to manage bamboo’s expansion. Regularly clear fallen leaves to maintain cleanliness and deter pests.
- Barriers for Runners: Employ metal or plastic barriers buried into the ground to keep runner bamboo in check and prevent it from overtaking your garden.
Conclusion:
Cultivating bamboo offers a unique opportunity to add beauty, privacy, and a touch of the exotic to your landscape. By understanding the distinctions between bamboo types and adhering to best planting and care practices, you can enjoy the many benefits of bamboo without the common pitfalls. With careful selection, preparation, and maintenance, your bamboo garden will thrive, transforming your outdoor space into a lush, green retreat.